
Domain 2 Quiz
Domain 2 Quiz
-
Decide where things go.
On the real test you will drag them and they snap into place.
4 cable locks with 4 laptops
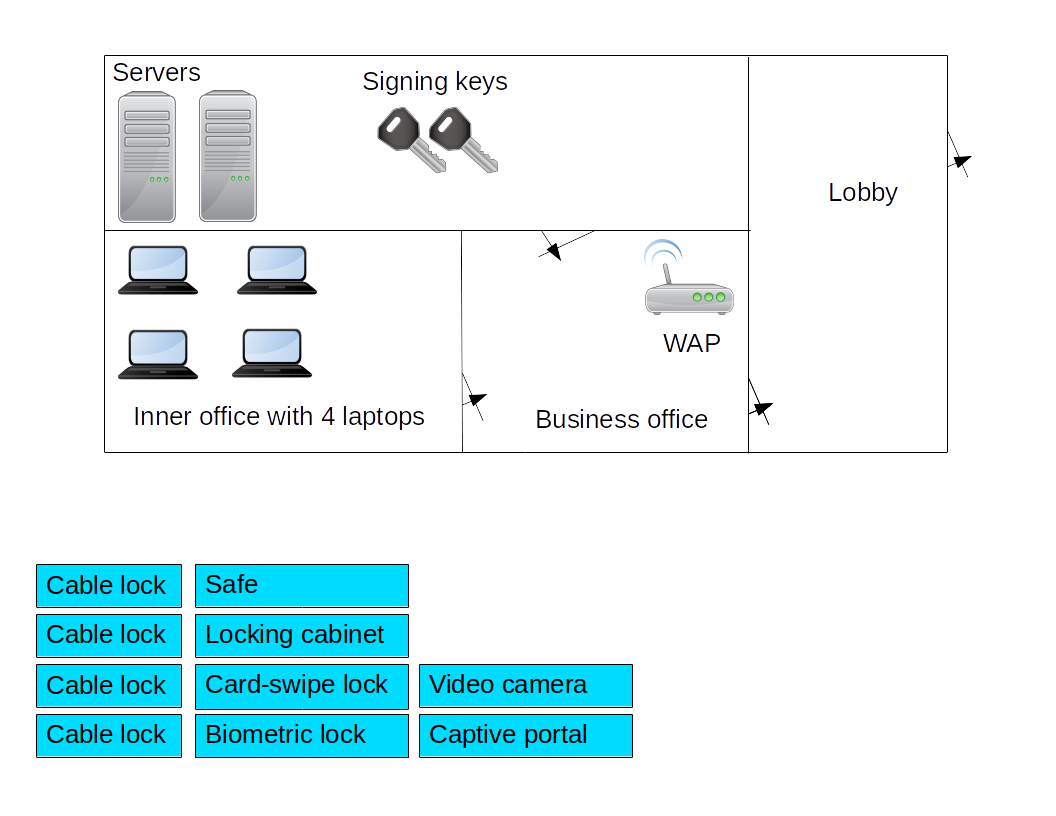
Safe with signing keys (these would be stored on optical discs or USB sticks)
Locking cabinet with WAP. (CompTIA says "locking cabinet" where I would say "equipment rack with locking doors", and yes, enclosing a WAP inside a metal cabinet makes no sense)
Card-swipe lock with door from lobby to business office. From public (sort of) area to business area.
Biometric lock with door from business office to server room. Most sensitive door, it gets the best lock.
Video camera in server room.
Captive portal with lobby. -
Jenny can unlock her work mobile phone by drawing a pattern
on the screen with her finger.
This mode of authentication verifies:
- Something you know
- Something you have
- Something you are
- Something you do
- Somewhere you are
-
To enter the server room Joe must pass through a mantrap,
entering a PIN on a keypad at the outer door,
entering the mantrap and closing the door behind him,
swiping his badge on the reader,
then typing a password into a keyboard by the inner door.
How many factors is this?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
To enter the server room Joe must
be recognized by the guard,
enter a PIN on the keypad,
and place his hand on a scanner.
How many factors is this?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
To enter the server room Joe must
be recognized by the guard,
show the guard his badge,
and enter a PIN on the keypad.
How many factors is this?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
Joe has been given a Post-It note with a PIN written on it.
To enter the server room he must
be recognized by the guard,
tell the guard the passphrase of the day,
and enter the PIN on the keypad.
How many factors is this?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
Beth, a system administrator, is training Jerry, a new
data maintenance technician, in how to restore backup
data into production use.
Which of the following should they be using?
- Recovery playbook
- Order of restoration
- Order of volatility
- Snapshot guidance
-
Dale is the manager of the software development group.
She has directed her programmers to make a backup of their
code and test data at the end of every day,
locking the media in a desk drawer,
and making sure to lock their office door.
What is the greatest remaining concern?
- Data remanence
- Off-site backups
- Data sovereignty
- Privacy protection
-
Lori's manager, Brian, has just returned from a board meeting
where it was announced that the company would be deploying
Infrastructure as a Service.
Brian didn't know what that was, and was embarrassed to ask.
Which is the best explanation of what it will involve?
- Logical rather than physical network isolation
- Air gaps
- Virtualization
- Subcontracting
-
Dorothy, the software development manager, needs development
and testing platforms for her programmers.
However, she doesn't want to have to buy server hardware,
or cross-train programmers to be system administrators.
Which cloud solution could solve her problem?
- IaaS
- IDaaS
- PaaS
- SaaS
-
Maria, a security analyst, was about to boot a suspect
system with a Kali Linux DVD.
Her manager stopped her, saying that she mustn't modify
the computer's operating system or data.
She explained that it was safe, it would load an
operating system into RAM and treat everything on disk
as read-only data, because it's:
- Non-modification boot
- Live boot
- Transparent boot
- Ephemeral boot
-
Alexei, an attacker from Eastern Europe, was able to break
into one of your organization's virtual web servers.
However, he was unable to pivot to any of several other
virtual servers running on the same hardware platform.
What benefit happened?
- VM Escape
- Shadow IT
- VM sprawl
- Sandboxing
- Hypervisor flaws
-
Abe, a security architect, needs to configure
Perfect Forward Secrecy for remote access for
employees working from home.
What can he use?
Select two.
- DH
- DHE
- ECDHE
- One-time pads
- AES-GCM-256
-
Charlotte is in charge of VPN access to the data analysis
facility.
She has read that it is helpful to pad a secret with a
short text value before encrypting it.
What concept is she considering?
- Salt
- Nonce
- Hash
- PBKDF2
-
International, national, and state/provincial regulations
require the protection of personal privacy.
This makes confidentiality important, but it is not
the only security goal.
You need to protect both endpoint authentication and
data confidentiality in all data streams.
Which ciphers should you choose?
Select two.
- AES-CBC
- AES-CCMP
- AES-CFB
- AES-GCM
-
Which of these are advantages of WPA/2 Enterprise
over WPA/2 PSK?
Select two.
- PKI
- Stronger cipher suite
- Higher performance
- Integrated Active Directory
- RADIUS
-
Tasha, a network engineer, is designing a wireless solution
for her large corporation.
She needs to specify the current best encryption,
supporting 802.1x with either LEAP or EAP-TLS.
What should she use?
Select three.
- CCMP
- AES-GCM-256
- WPA/2 PSK
- WPA/2 Enterprise
- RADIUS
- Active Directory
WPA/2 Enterprise uses a RADIUS server and certificates, while WPA/2 PSK uses manually configured pre-shared keys.
RADIUS is a trusted third party authentication service commonly used with 802.1x, it can speak several EAP variants. -
Blake has been asked to configure the web server to provide
Perfect Forward Secrecy.
Which security feature will this provide?
- Data sent from the server to the client will always be protected
- Data sent from the client to the server will always be protected
- A breach today does not expose keys from the past
- A breach today does not expose keys in the future
-
Alice wants to send an encrypted message to Bob.
What does she need?
- Alice's public key
- Alice's private key
- Bob's public key
- Bob's private key
Goal Sender needs Receiver needs Encrypted only Receiver's public key Receiver's private key Encrypted and signed Sender's private key
Receiver's public keySender's public key
Receiver's private keySigned only Sender's private key Sender's public key -
Alice must send a message which only Bob can read.
What does Alice need?
- Alice's private key
- Alice's public key
- Bob's private key
- Bob's public key
Exhibit with 10 things,
plus 19 regular questions
Passing = 82% of 29 = 23.8
Goal = 91% of 29 = 26.4