
Domain 3 Quiz
Domain 3 Quiz
-
Decide where things go.
WAF on web server.
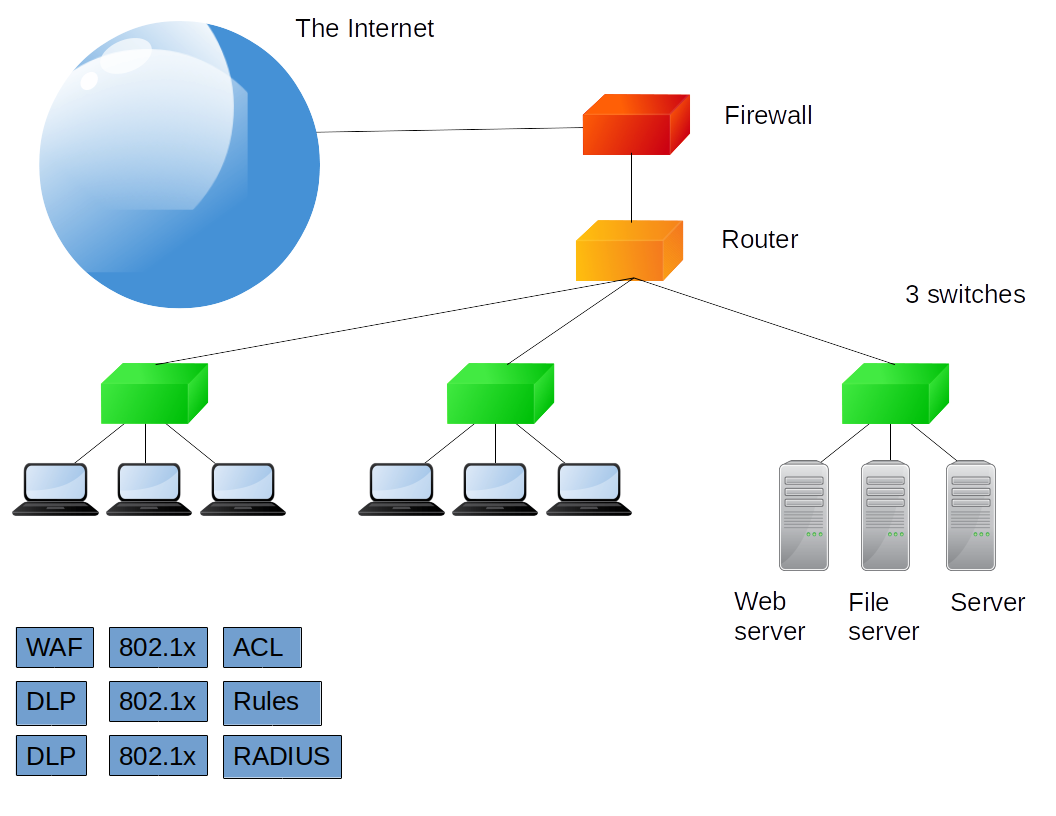
DLP on firewall. In a later quiz I say DLP goes either at a perimeter firewall or on endpoints, or workstations. But we have just two. Putting DLP on just one or two workstations out of six is wrong. The idea is really "On what type of device does this go?", it's all or none. I don't have two workstations, or two border firewalls, so I picked firewall and file server on the exam, and I think it was graded as correct.
DLP on file server.
3 802.1x on 3 switches.
ACL on router.
Rules on firewall.
RADIUS on spare server. -
Your CEO has met with the CEO of another company, and
they have agreed to work together to develop a new service.
Authentication and identity management will be connected
across the two organizations.
Given the sensitivity of the development project,
user authentication and authorization will use a centralized
server running the best available trusted third-party service.
Users will receive identity and service tokens
from a unified authentication and authorization service,
which requires that system clocks be synchronized
across the organizations.
Applications will be limited to those written with the
API of that service.
What do you need?
- BPA
- Federation
- Kerberos
- KDC
- NTP
- Kerberization
- BPA = the CEOs met
- Federation = connecting IAM
- Kerberos = best available 3rd party authentication service
- KDC = Key Distribution Center, the Kerberos server
- NTP = Network Time Protocol
- Kerberization = (re)writing an application with the Kerberos API, making it Kerberized
-
The content management group is considering the use of
DNS Round Robin technology.
What benefit could this provide?
- Load balancing
- Transparent proxying
- Anti-spoofing
- Certificate sharing
As a practical example, at one time www.jpl.nasa.gov resolved to a list of IP addresses, one server at each major NASA facility in the US. The list you got was in an arbitrary order, and your browser used the first on in the list. It worked, you saw the images from the current mission, and all NASA web servers had roughly equal loads. -
Users are reporting that they can't access the financial
department's secure web page.
The following command output is observed.
What is wrong?
$ netstat -an Active Internet connections (including servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address (state) tcp4 0 0 10.138.0.3:22 184.16.205.240:50966 ESTABLISHED tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1:9000 127.0.0.1:37632 TIME_WAIT tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1:11628 127.0.0.1:9000 TIME_WAIT tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1:12042 127.0.0.1:9000 TIME_WAIT tcp4 0 0 10.138.0.3:80 130.15.4.209:46944 TIME_WAIT tcp4 0 0 10.138.0.3:80 46.229.168.70:15234 TIME_WAIT tcp4 0 0 10.138.0.3:80 173.187.65.22:50598 ESTABLISHED tcp4 0 0 10.138.0.3:80 212.3.84.1:55989 ESTABLISHED tcp4 0 0 10.138.0.3:80 212.3.84.1:55987 ESTABLISHED tcp4 0 0 10.138.0.3:80 212.3.84.1:55988 TIME_WAIT tcp4 0 0 10.138.0.3:80 212.3.84.1:55986 TIME_WAIT tcp4 0 0 *:80 *.* LISTEN tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1:9000 *.* LISTEN tcp4 0 0 *:22 *.* LISTEN tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 *.* LISTEN udp4 0 0 127.0.0.1:123 *.* udp4 0 0 10.138.0.3:123 *.* udp4 0 0 *:123 *.* udp4 0 0 *:514 *.*
- The web server is down
- The server is up but its web service isn't running
- The certificate is expired
- The certificate has been revoked
- HTTPS isn't enabled
- A firewall is blocking connections
This is real output, copy and paste from a connection to my web server, but with listening HTTPS removed and all instances of TCP/443 changed to TCP/80. My server is at Google, in a 10.38.0.0/24 VLAN. -
Which of these can you put in a boot script to
prevent MitM?
-
nmap -sS -sV -T5 192.168.12.72 -
arp -s 00:13:3B:12:6f:aa 192.168.12.72 -
tcpdump -i eth0 host 192.168.12.72 or ether host 00:13:3b:12:6f:aa -
netstat -an -
ping 192.168.12.72
arpsyntax sets up static ARP, it's that same syntax on Windows, Linux, MacOS, BSD, and probably other places. Static ARP isn't at all practical, but it could prevent MitM connection hijacking with ARP spoofing. Once you set a static ARP mapping, the operating system no longer uses ARP to make requests, or pays attention to inbound unsolicited ARP "answers". The other commands arenmap(port scanning and OS detection),tcpdump(packet capture),netstat(measuring TCP/UDP activity), andping(testing end-to-end IP connectivity). Static ARP is the only one that has any preventative function. -
-
You are examining records from a busy server that is
critical to your organization's financial well-being.
You find this:
LAST WEEK: /boot/grub/grub.cfg: 6c3209882734351aa672d3f222bb382267c22ad4 /boot/vmlinuz-4.13.0: d6328ceea77c930e853da08b494c71ad2f8f9b47 /etc/passwd: 02f727aaabab9c2963092ba3d7f3543980fef790 /etc/shadow: 71558dd386a50333ffb71c07ad904e9abd6792cf /etc/ssh/sshd_config: 5a960d6641b42ff8f9e947e218b371b2ad12a728 /bin/ls b79f70b18538de0199e6829e06b547e079df8842 TODAY: /boot/grub/grub.cfg: 6c3209882734351aa672d3f222bb382267c22ad4 /boot/vmlinuz-4.13.0: d6328ceea77c930e853da08b494c71ad2f8f9b47 /etc/passwd: 02f727aaabab9c2963092ba3d7f3543980fef790 /etc/shadow: 9a4fb74ef00824d6e84785ad53d6fed364947778 /etc/ssh/sshd_config: 5a960d6641b42ff8f9e947e218b371b2ad12a728 /bin/ls b79f70b18538de0199e6829e06b547e079df8842
What should you report to management?- Everything seems to be fine.
- A user is violating the AUP.
- An intruder has gained administrative access and changed the system configuration.
- An intruder has gained administrative access and replaced operating system components, and we can no longer trust the operating system itself or any programs installed there.
/etc/shadowchanged, but we expect this. It will change every time a user changes their password. Apparently "busy" implies enough users that we caught someone changing their password between yesterday's and today's Tripwire run. -
You are examining records from a busy server that is
critical to your organization's financial well-being.
You observe this:
LAST WEEK: /boot/grub/grub.cfg: 6c3209882734351aa672d3f222bb382267c22ad4 /boot/vmlinuz-4.13.0: d6328ceea77c930e853da08b494c71ad2f8f9b47 /etc/passwd: 02f727aaabab9c2963092ba3d7f3543980fef790 /etc/shadow: 71558dd386a50333ffb71c07ad904e9abd6792cf /etc/ssh/sshd_config: 5a960d6641b42ff8f9e947e218b371b2ad12a728 /bin/ls b79f70b18538de0199e6829e06b547e079df8842 TODAY: /boot/grub/grub.cfg: 6c3209882734351aa672d3f222bb382267c22ad4 /boot/vmlinuz-4.13.0: d6328ceea77c930e853da08b494c71ad2f8f9b47 /etc/passwd: 02f727aaabab9c2963092ba3d7f3543980fef790 /etc/shadow: 71558dd386a50333ffb71c07ad904e9abd6792cf /etc/ssh/sshd_config: 9c5bbcbdc2994a9835b8804b9ffa699935715a34 /bin/ls b79f70b18538de0199e6829e06b547e079df8842
What should you report to management?- Everything seems to be fine.
- A user is violating the AUP.
- An intruder has gained administrative access and changed the system configuration.
- An intruder has gained administrative access and replaced operating system components, and we can no longer trust the operating system itself or any programs installed there.
/etc/ssh/sshd_config. -
You are examining records from a busy server that is
critical to your organization's financial well-being.
You observe this:
LAST WEEK: /boot/grub/grub.cfg: 6c3209882734351aa672d3f222bb382267c22ad4 /boot/vmlinuz-4.13.0: d6328ceea77c930e853da08b494c71ad2f8f9b47 /etc/passwd: 02f727aaabab9c2963092ba3d7f3543980fef790 /etc/shadow: 71558dd386a50333ffb71c07ad904e9abd6792cf /etc/ssh/sshd_config: 5a960d6641b42ff8f9e947e218b371b2ad12a728 /bin/ls b79f70b18538de0199e6829e06b547e079df8842 TODAY: /boot/grub/grub.cfg: 6c3209882734351aa672d3f222bb382267c22ad4 /boot/vmlinuz-4.13.0: cfc34c90281bbed47540c6288ec975a4602ee3df /etc/passwd: 02f727aaabab9c2963092ba3d7f3543980fef790 /etc/shadow: 71558dd386a50333ffb71c07ad904e9abd6792cf /etc/ssh/sshd_config: 5a960d6641b42ff8f9e947e218b371b2ad12a728 /bin/ls b79f70b18538de0199e6829e06b547e079df8842
What should you report to management?- Everything seems to be fine.
- A user is violating the AUP.
- An intruder has gained administrative access and changed the system configuration.
- An intruder has gained administrative access and replaced operating system components, and we can no longer trust the operating system itself or any programs installed there.
-
Management has decided that they want wireless security,
but they don't have the resources to do key management
and maintain certificates.
What should they use?
- WEP
- WAP
- WPA
- WPA2 Enterprise
- WPS
-
Management has decided to use geo-fencing to restrict
mobile device operation to company premises.
Which technology should you select?
- BYOD
- COPE
- CYOD
- BODE
-
You observe the following in the results of a security scan.
What is this?
Channel SSID 1 corpnet36 corpnet36 netgear11 corpnet3- Evil twin
- Rogue AP
- Bluesnarfing
- Watering hole
-
Desmond, a network engineer, has been directed to set up
network security that will require a device to authenticate
itself onto the network and verify that patching and
anti-virus signatures are updated, before allowing the
user to try to authentication.
What should Desmond use?
- 802.1i
- 802.1x
- 802.1q
- 802.11i
-
You observe the following in the results of a security scan.
What is this?
Channel SSID 1 corpnet36 corpnet36 corpnet311 corpnet3- Evil twin
- Rogue AP
- Bluesnarfing
- Watering hole
In case Bob hasn't remembered to tell you this part yet...
The three useful channels (in the CompTIA universe) are 1, 6, and 11. If you get a "configure this network" diagram involving wireless, carefully look all around it to see what fixed wireless is already there.
If you are configuring the only WAP, use channel 6 as it's the middle of the band and the antenna(s), always a compromise, will work best there.
If you are configuring an additional WAP, and there's already just one on either channel 1 or 11, pick the opposite end.
If there are two others, pick whichever of 1, 6, and 11 aren't yet in use. -
You observe this data.
An unapproved executable attempted to run and was prevented. The action was stopped and logged. Location: c:\Program Files\Chromium Browser\Chrome.exe User: Elon Cause: Policy setting for unapproved softwareWhich tool or defensive measure was involved?- File integrity check
- Antivirus
- Blacklisting
- Whitelisting
- DLP
- DEP
-
Julie, a network engineer, has been informed by management
that they want to deploy network security technology that
uses OSI layers 4 through 7 to authenticate, authorize, and audit Internet activity. To reduce the load on help desk personnel, this must require little to no browser or other application reconfiguration. What should she recommend?
- SIEM
- 802.1x
- Transparent proxy
- Load balancer
-
Jenny can unlock her work mobile phone by drawing a pattern
on the screen with her finger.
This mode of authentication verifies:
- Something you know
- Something you have
- Something you are
- Something you do
- Somewhere you are
-
To enter the server room Joe must pass through a mantrap,
entering a PIN on a keypad at the outer door,
entering the mantrap and closing the door behind him,
swiping his badge on the reader,
then typing a password into a keyboard by the inner door.
How many factors is this?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
To enter the server room Joe must
be recognized by the guard,
enter a PIN on the keypad,
and place his hand on a scanner.
How many factors is this?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
To enter the server room Joe must
be recognized by the guard,
show the guard his badge,
and enter a PIN on the keypad.
How many factors is this?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
Joe has been given a Post-It note with a PIN written on it.
To enter the server room he must
be recognized by the guard,
tell the guard the passphrase of the day,
and enter the PIN on the keypad.
How many factors is this?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
Kristina works at a financial services firm that suffered a
major breach.
They have implemented a centralized AAA system regulating
access to the Intranet.
After proving their identity with a smart card and a
complex passphrase, users are connected to the appropriate
VLAN.
Internal services are only provided to user sessions holding
valid service tickets.
Intranet activity records are continuously analyzed to
detect inappropriate or malicious activity.
Identify this latter activity.
- Identification
- Authentication
- Authorization
- Auditing
-
Akira authenticates with a device that displays a different
value every minute.
What is this an example of?
- Multi-factor
- OTP
- HOTP
- TOTP
-
Kerberos provides which three of the following?
Select three.
- Network intrusion detection
- ESSO
- Cryptographic key control
- Log analysis and alerting
- An API supporting third-party applications
- A "single pane of glass" dashboard
-
Functional SSO must incorporate which of the following?
- Active Directory
- RADIUS
- Federated identity management
- Kerberos
-
Which of these is an XML-based open-source standard that
involves an IdP or Identity Provider,
an SP or Service Provider, and a Principal,
and is the basis for several other authentication systems?
- SAML
- OAUTH
- OpenID
- Shibboleth
- WS-Federation
-
You are equipping a forensics team.
Which of these would be most useful?
- A set of precision screwdrivers
- A playbook
- Luminol
- Latex gloves and masks
-
You observe this data.
11:43:57.293662 IP 192.168.1.1 > 192.168.1.7: ICMP echo request, id 5331, seq 1, length 64 11:43:57.294143 IP 192.168.1.7 > 192.168.1.1: ICMP echo reply, id 5331, seq 1, length 64 11:43:58.294308 IP 192.168.1.1 > 192.168.1.7: ICMP echo request, id 5331, seq 2, length 64 11:43:58.294730 IP 192.168.1.7 > 192.168.1.1: ICMP echo reply, id 5331, seq 2, length 64 11:43:59.322328 IP 192.168.1.1 > 192.168.1.7: ICMP echo request, id 5331, seq 3, length 64 11:43:59.322645 IP 192.168.1.7 > 192.168.1.1: ICMP echo reply, id 5331, seq 3, length 6
Which tool or defensive measure was involved? Select two.- Wireshark
- ping
- nmap
- tcpdump
- netstat
- arp
- ifconfig
tcpdump, which you could also get by saving Wireshark output to a text file (or running the text-output version,tshark). Yes, apingcommand was running to generate this traffic, but its output is different. -
You observe this data.
www.google.com (172.217.6.4) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from ord38s01-in-f4.1e100.net (172.217.6.4): icmp_seq=1 ttl=116 time=26.9 ms 64 bytes from ord38s01-in-f4.1e100.net (172.217.6.4): icmp_seq=2 ttl=116 time=28.2 ms 64 bytes from ord38s01-in-f4.1e100.net (172.217.6.4): icmp_seq=3 ttl=116 time=27.2 ms 64 bytes from ord38s01-in-f4.1e100.net (172.217.6.4): icmp_seq=4 ttl=116 time=27.2 ms 64 bytes from ord38s01-in-f4.1e100.net (172.217.6.4): icmp_seq=5 ttl=116 time=28.5 ms --- www.google.com statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 received, 0% packet loss, time 4005ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 26.976/27.673/28.568/0.621 ms
Which tool or defensive measure was involved?- Wireshark
- ping
- nmap
- tcpdump
- netstat
- arp
- ifconfig
pingoutput with its name removed. On the test you can go back, so if you realize that this ispingoutput while earlier that must have beentcpdumpcapture of it, you can go back and change your answer. -
You observe this data.
Host is up (0.00031s latency). rDNS record for 192.168.1.40: hplj4250n.kc9rg.org Not shown: 993 closed ports PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 80/tcp open http Virata-EmWeb 6.2.1 (HP LaserJet http config) 280/tcp open http Virata-EmWeb 6.2.1 (HP LaserJet http config) 443/tcp open ssl/https? 515/tcp open printer 7627/tcp open http HP-ChaiSOE 1.0 (HP LaserJet http config) 9100/tcp open jetdirect? 14000/tcp open tcpwrapped MAC Address: 00:12:79:DF:81:B1 (Hewlett Packard) Device type: printer Running: HP embedded OS details: HP LaserJet 4250 (JetDirect) printer Network Distance: 1 hop Service Info: Host: 192.168.1.40; Device: printer
Which tool or defensive measure was involved?- Wireshark
- ping
- nmap
- tcpdump
- netstat
- arp
- ifconfig
nmapoutput, with the first and last lines showing its own name removed. I scanned my laser printer. -
You want to use a system that can protect communication
by authenticating the server, and also providing
a copy of the server's public key in a trustworthy format.
A provider of trusted certificates will only provide one
when you follow their rules.
There is a protocol that you can use to check in real time
whether a certificate should be trusted or not.
You must have a copy of the currently untrusted
certificates locally, to reduce network traffic.
Rather than a complete copy of the key,
you may refer to its hash instead.
There are ways to prevent a breach today from exposing
secrets based on keys in the past.
What do you need?
- TLS
- CPS
- OCSP
- CRL
- thumbprint
- PFS
"a system that can ..." = TLS or Transport Layer Security
"the rules" = CPS or Certificate Practices Statement
"a protocol" = OCSP or Online Certificate Status Protocol
"copy of the revoked keys" = CRL or Certificate Revocation List
"its hash" = thumbprint
"exposure today doesn't expose keys from the past" = PFS or Perfect Forward Secrecy
"What do you need?" is the actual question. One of the sentences says "You must have", it's a requirement. The others state that the item provides some feature, or describe your plan.
The requirement is for a local copy of the CRL, which is a relatively uncommon or unneeded step. This makes it a better question from the CompTIA point of view. Less common makes it more challenging. -
Blake has been asked to configure the web server to provide
Perfect Forward Secrecy.
Which security feature will this provide?
- Data sent from the server to the client will always be protected
- Data sent from the client to the server will always be protected
- A breach today does not expose keys from the past
- A breach today does not expose keys in the future
-
Alice wants to send an encrypted message to Bob.
What does she need?
- Alice's public key
- Alice's private key
- Bob's public key
- Bob's private key
That table answers a lot of questions in the Domain 6 pool.Goal Sender needs Receiver needs Encrypted only Receiver's public key Receiver's private key Encrypted and signed Sender's private key
Receiver's public keySender's public key
Receiver's private keySigned only Sender's private key Sender's public key -
Alice has obtained a copy of Bob's certificate.
Which of these does it contain?
- Bob's private key
- Bob's public key
- The CA's private key
- The CA's public key
-
Alice has obtained a copy of what claims to be
Bob's certificate.
Which of these does she need to verify that it really
belongs to Bob?
- Bob's private key
- Bob's public key
- The CA's private key
- The CA's public key
-
Bob has just received an digitally signed, encrypted message
from Alice.
What does he need?
Select three.
- Alice's certificate
- Bob's certificate
- The CA's certificate
- Bob's public key
- Bob's private key
Then he needs his private key to decrypt the content. (which she encrypted with a copy of his public key, which was in his certificate, etc.)
I'm sure that I am giving CompTIA far too much credit, implying that they would get this complete and correct. But if you understand the above, you're doing well. Expect this to be simpler, choosing just these two of four:- Alice's public key
- Alice's private key
- Bob's public key
- Bob's private key
Exhibit with 9 things,
plus 34 regular questions
Passing = 82% of 43 = 35.3
Goal = 91% of 43 = 39.1